Workflows for pangenomics
Since PanTools has many subcommands, we have created a number of workflows to help you get started.
Finding core, accessory and unique genes
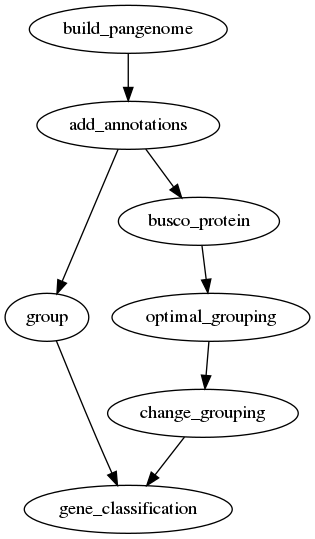
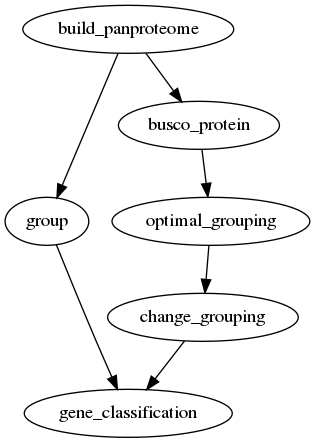
One of the most common tasks for a pangenome analysis is to find the core,
accessory and unique genes in a set of genomes. For this, one needs to
calculate homology groups and then find the core, accessory and unique genes.
Homology grouping can be done using the group command if one already has
a set of parameters for the homology search. If not, the optimal_grouping
command can be used to find the optimal parameters for a given set of
proteins. This core, accessory and unique analysis can be performed for both
pangenomes and panproteomes.
Pangenome analysis
Panproteome analysis
Creating phylogenetic trees
PanTools has six different commands for creating phylogenetic trees. However, some methods are specific to a pangenome since they work on nucleotide sequences. Optionally, one can also add phenotype information to the PanTools database and use this information to color the tree.
Pangenome analysis
![digraph G {
"build_pangenome" -> "add_annotations";
"build_pangenome" -> "add_phenotype" [style=dashed];
"add_annotations" -> "group";
"add_annotations" -> "busco_protein";
"busco_protein" -> "optimal_grouping";
"optimal_grouping" -> "change_grouping";
"group" -> "gene_classification";
"change_grouping" -> "gene_classification";
"add_phenotype" -> "gene_classification" [style=dashed];
"gene_classification" -> "gene_distance_tree.R";
"add_phenotype" -> "kmer_classification" [style=dashed];
"build_pangenome" -> "kmer_classification";
"add_phenotype" -> "ani" [style=dashed];
"build_pangenome" -> "ani";
"kmer_classification" -> "genome_kmer_distance_tree.R";
"gene_classification" -> "core_phylogeny";
"gene_classification" -> "mlsa_find_genes";
"mlsa_find_genes" -> "mlsa_concatenate";
"mlsa_concatenate" -> "mlsa";
"gene_classification" -> "consensus_tree";
}](../_images/graphviz-5310005e662672fa4c98207a74d31790f6a79965.png)
Panproteome analysis
![digraph P {
"build_panproteome" -> "add_phenotype" [style=dashed];
"build_panproteome" -> "group";
"build_panproteome" -> "busco_protein";
"busco_protein" -> "optimal_grouping";
"optimal_grouping" -> "change_grouping";
"group" -> "gene_classification";
"change_grouping" -> "gene_classification";
"add_phenotype" -> "gene_classification" [style=dashed];
"gene_classification" -> "gene_distance_tree.R";
"add_phenotype" -> "kmer_classification" [style=dashed];
"build_panproteome" -> "kmer_classification";
"add_phenotype" -> "ani" [style=dashed];
"build_panproteome" -> "ani";
"kmer_classification" -> "genome_kmer_distance_tree.R";
"gene_classification" -> "core_phylogeny";
"gene_classification" -> "mlsa_find_genes";
"mlsa_find_genes" -> "mlsa_concatenate";
"mlsa_concatenate" -> "mlsa";
"gene_classification" -> "consensus_tree";
}](../_images/graphviz-1016203715c09dc1740710911ec99b497520c488.png)
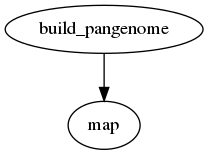
Mapping reads
PanTools has a map subcommand for mapping WGS reads to a pangenome. This
subcommand can be used to map reads to a pangenome only.